You’ve likely seen the term ICT trading mentioned on forex trading websites, blogs, or in online communities. Even though it has been around for several years, it has recently started to attract a lot more attention in the trading world.
ICT stands for Inner Circle Trading, but that probably doesn’t tell you a lot. In the following sections, we’ll explain exactly what this strategy involves.

What Is the ICT Trading Strategy?
The ICT strategy is a structured method for trading forex that brings technical analysis together with an emphasis on market behavior. If you use this strategy, you will be looking for key price levels and patterns that signal potential opportunities to profit.
The strategy also incorporates knowledge of institutional trading movements, which helps traders anticipate where major players are likely to position themselves.
What is an ICT trader?
An ICT trader is someone who follows the Inner Circle Trading strategy.
A key element of being an ICT trader is focusing on trading psychology — the skill of managing your emotional responses and remaining disciplined. To uphold trading discipline, the strategy establishes specific guidelines for trade size, exit points, and well-defined rules to help avoid erratic decisions leading traders off course.
Basic principles and objectives of the ICT trading strategy
The ICT strategy was developed by Michael J. Huddleston.
A sophisticated approach to forex trading that represents the actions of large institutional players on the market, it enables retail traders to gauge market movements by learning and mimicking the forex trading strategies used by these institutions. This method is developed through an in-depth study of market structure, order flow, and price action.
Key components of the ICT trading strategy
ICT strategies include a number of components that are necessary for spotting potential trading setups and projecting market behavior. These collectively represent several frameworks for traders, including order blocks, fair value gaps, liquidity pools, and much more.
A brief overview of trading strategies
This trading strategy performs an essential function: giving traders a system for making trading decisions. The ICT trading strategy is particularly notable for its detailed analysis of market cycles, which helps traders handle the complexities of financial markets. Traders who are good at using this strategy have a considerable lead over their competition.
How does the ICT trading strategy work?
The ICT trading strategy covers a number of concepts: market structure, optimal trade entry points, and the significance of various trading sessions. These make you better at forecasting market movements by helping you understand what drives them. Traders need to master these concepts to apply the method effectively.
First, market structure helps traders see the overall trend and key price levels, so they can tell if the market is likely to keep moving in the same direction or if a reversal might happen. Next, based on certain price patterns that signal a good opportunity, optimal trade entry points help them spot the best moment to jump into a trade. Finally, understanding trading sessions is essential for choosing the right hours to trade, and what to trade at what time.
Key ICT trading concepts
|
Market structure
|
Price levels (highs/lows) that shape market behavior
|
|
Liquidity zones
|
Areas with significant buy/sell orders that affect price
|
|
Smart money concepts
|
Concepts that focus on institutional traders’ actions and market impact
|
|
Order flow analysis
|
Involves analyzing orders to understand supply and demand
|
|
Price action trading
|
Making choices shaped by price movements, no indicators
|
|
Fair value gap
|
Identifying price deviations for trade opportunities
|
|
Optimal trade entry
|
Entering trades at the best price points
|
|
Order blocks
|
Support and resistance levels where institutions place large orders
|
|
Kill zones
|
High-movement times during trading sessions
|
|
Asian session range
|
The price range set in the Asian session, which impacts later sessions
|
Some of these concepts require further explanation, and others have yet to be mentioned. Let’s dive deeper.
Fair value gap
The fair value gap (FVG), also known as imbalance, is critical to the ICT forex trading strategy. The term refers to a price gap created by an imbalance in buying or selling, often leading to a robust price movement away from its fair value. These gaps typically get filled as the market seeks a balance and gives traders possible entry and exit strategies.
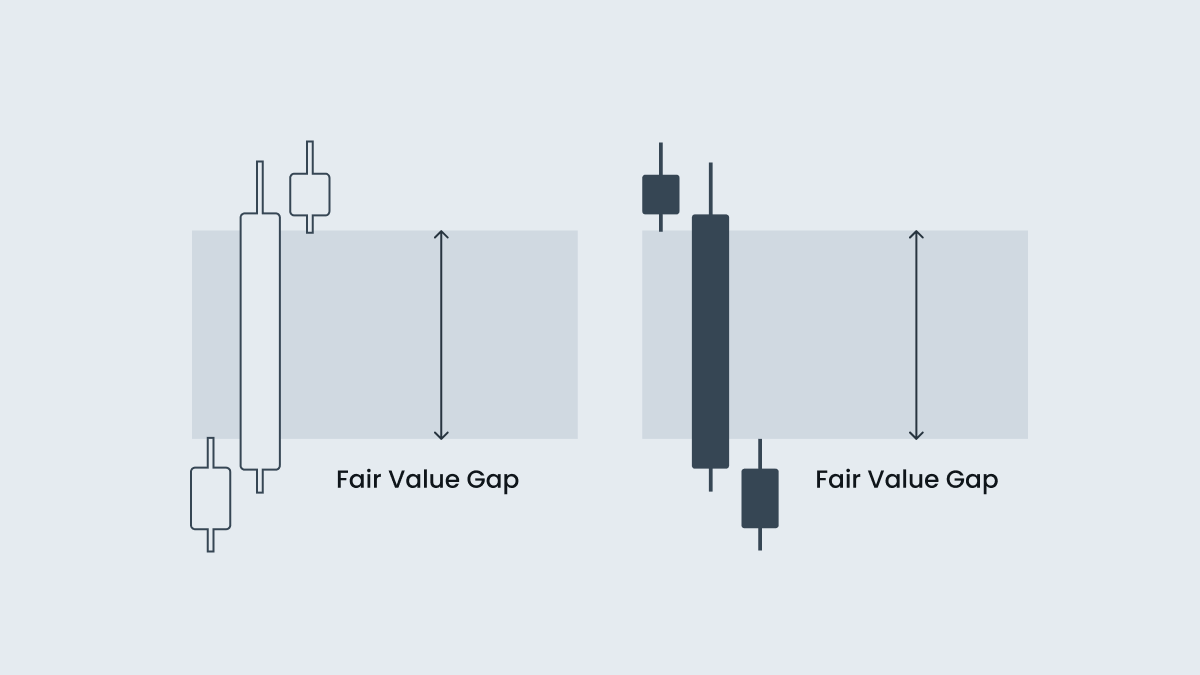
FVG is usually presented on a price chart as a three-candlestick pattern. In a bullish scenario:
-
The upper wick of the first candle does not connect to the lower wick of the third candle.
-
The gap (on the second candle) created by the wicks of the first and third candles is called the fair value gap.
In a bearish scenario, the pattern is reversed, with the lower wick of the first candle not connecting to the upper wick of the third candle.
The market tries to fill this imbalance zone (FGV), acting like a magnet for the price. By recognizing these gaps, traders can anticipate potential price reactions and plan their entries and exits.
.png)
To enter a short trade, wait for the price to sweep the closest liquidity pool and reverse, leaving the FVG behind, as shown in the chart above.
Optimal trade entry balanced price range
Optimal trade entry is another crucial component of the ICT strategy. This concept involves identifying the balanced price range — a zone that the market will retest before resuming its trend.
These levels are significant in that they matter to institutional participants. For example, the price impulsing at a given level suggests that a large trade was executed, or significant stop-loss or take-profit order types were triggered. Prices often return to these impulse points, which makes them optimal entry points.
Another way to understand the optimal trade entry (OTE) is based on the fact that, during an uptrend, traders prefer to trade from the long side. To do this effectively, they look for a correction in the uptrend that is deep enough to offer an optimal risk-reward ratio, but not so deep that it breaks the trend. These corrections, often called OTEs, typically align with imbalances, order blocks, or retracements below the 0.618 Fibonacci level, ensuring optimal entry by capitalizing on the natural pullback and maintaining trend power.
.png)
To identify the balanced price range (BPR) zone, you have to mark a fair value gap on the sell side of the price and another one on the buy side (or opposite in the reverse situation).
These fair value gaps are horizontally aligned with each other.
Now find and mark the price area where both fair value gaps overlap.
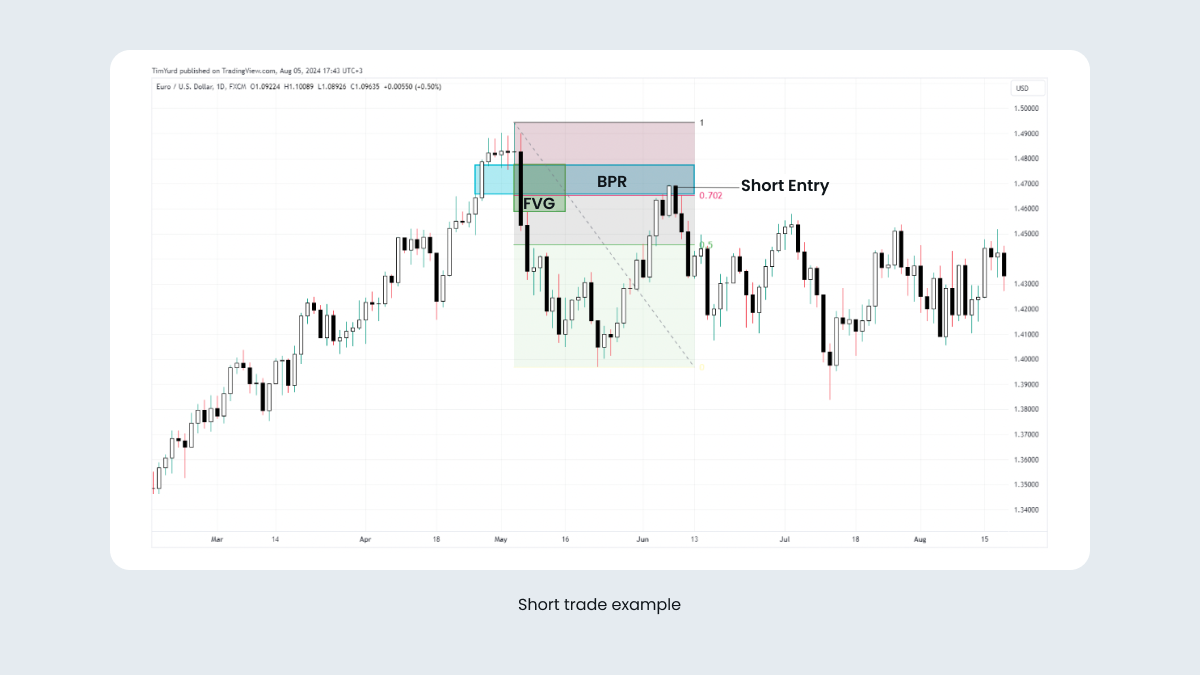
In a case like this, the value 0.702 Fibo will help you open trades with a better risk/profit ratio.
In the example above, you can see how the price reverses downwards when the BPR zone at 0.702 Fibonacci is reached.
Order blocks
Order blocks are supply and demand zones where institutional market participants and retail traders place large orders. Since a large order can cause a robust price change, it is broken down into smaller order blocks executed as counter orders accumulate liquidity. These steps allow institutional traders to fully execute a large order without significantly affecting the price.
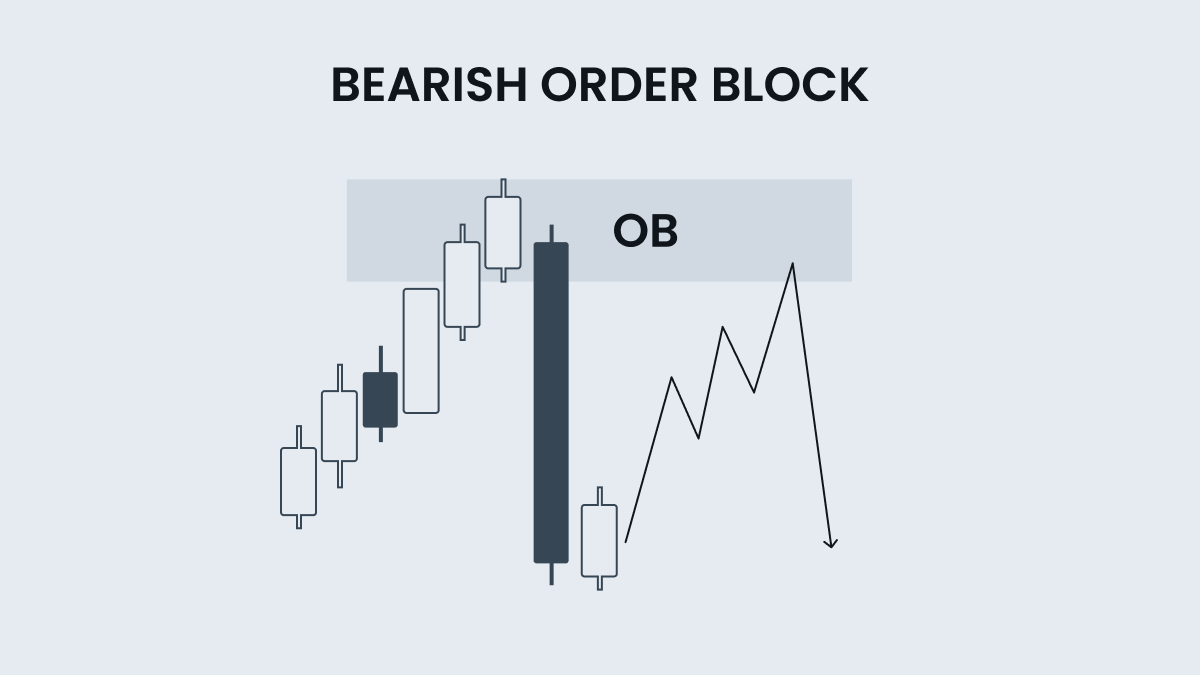
The bearish OB often resembles the last bullish candle before a decline, or a bearish candle before a rise, depending on which reversal you are looking for.
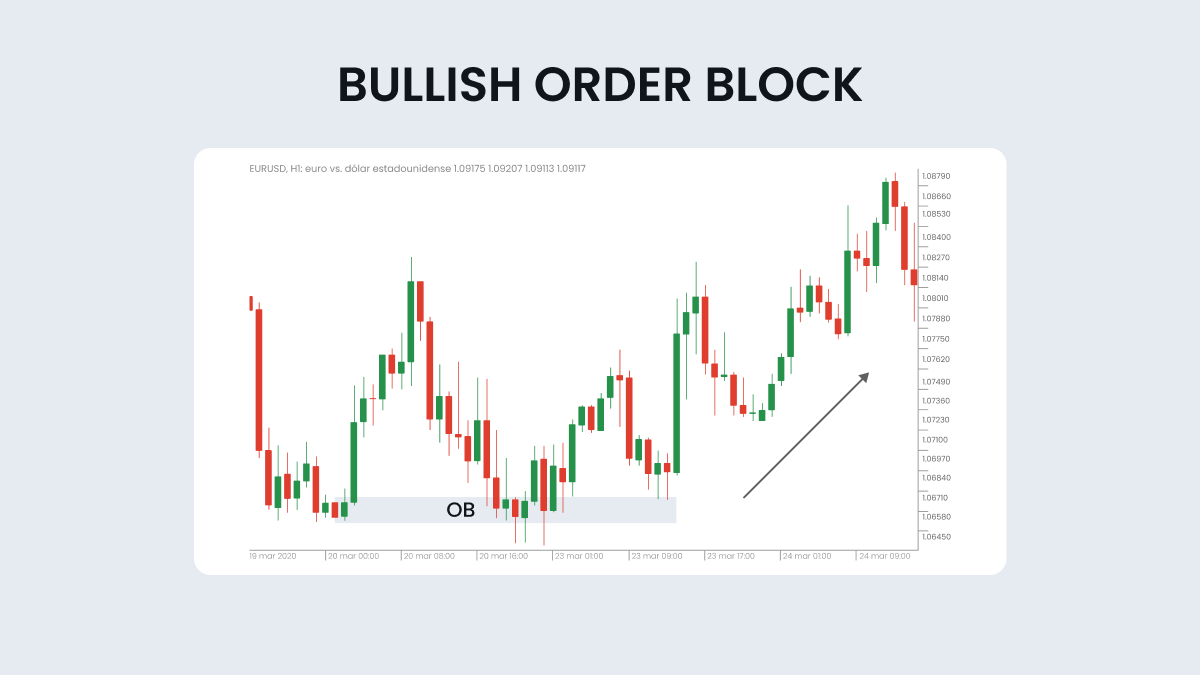
When identifying order blocks, the senior timeframe is a crucial aspect to include in the chart. For example, a daily order block (OB) is much more significant than a 4-hour OB. Higher timeframe order blocks generally have a stronger influence and retracement on price action and are more reliable for making trading decisions.
Kill zones
Kill zones represent a specific time period of the day when the market is especially likely to demonstrate certain predictable movements. These periods include the Asian Session, the London Open, and the New York Open.
Asian session range
The Asian session range, from 3:00 a.m. to 12:00 p.m. (GMT+3), is a very important period in the ICT strategy because it often shows a market consolidation, which sets up potential trade opportunities for the more volatile London and New York sessions.
.png)
In the higher timeframes, you can use the ICT Asian range to forecast price action following the session. A tight consolidation within the Asian range typically signals an upcoming trend shift where the market will likely sweep out liquidity either above or below this range. This liquidity sweep traps retail traders into trading in the wrong direction, after which the price often reverses.
London open momentum
.png)
The London Open is well known for its high volatility and significant price movements, especially during the London open kill zone from 09:00 a.m. to 12:00 p.m. (GMT +3). This period is good for trading EUR and GBP currency pairs, as it carries great potential for high profitability.
The London session has the best potential for substantial directional movement. If the daily trend is upward, traders can use this session to identify the trading day’s low and high. Typically, the high or low of the day forms during the London session, making it a critical period for executing trades based on the overall daily trend.
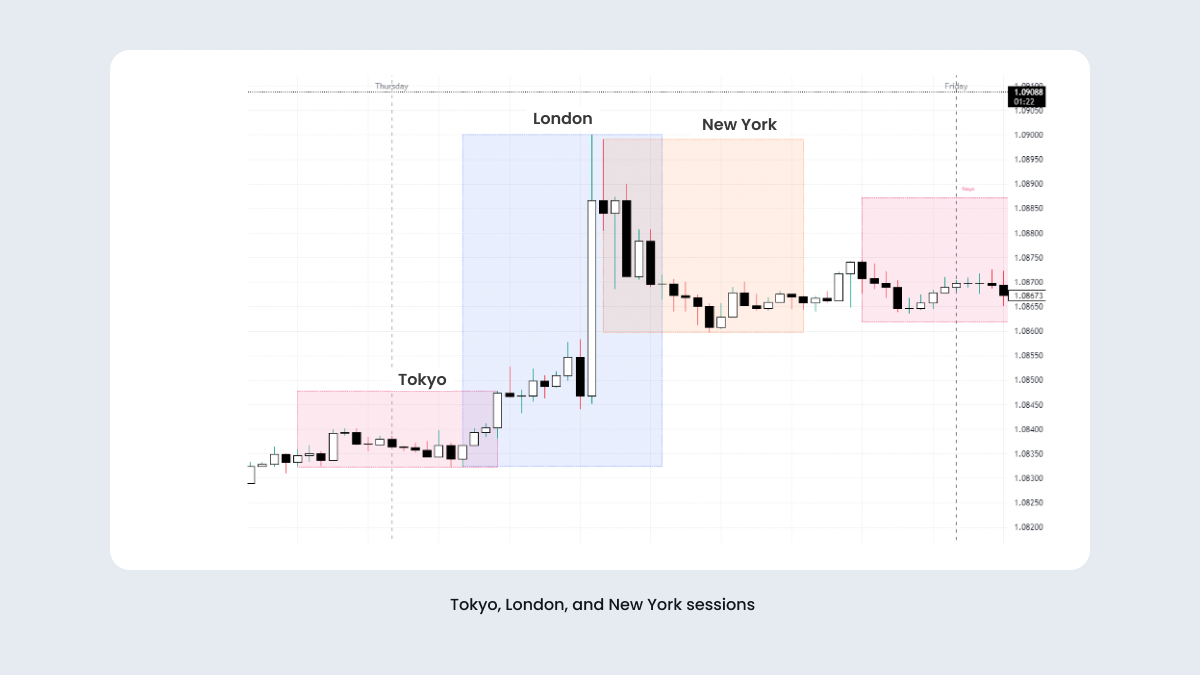
New York session volume profile
From the volume analysis perspective, the New York kill zone, from 1:00 p.m. to 4:00 p.m. GMT in winter and from 12:00 p.m. to 3:00 p.m. GMT in summer, is crucial for USD-paired currencies and almost all the markets.
This window marks the overlap of the London and New York sessions, resulting in heightened volatility due to the simultaneous activity of traders from both continents.
During this time, traders seek either the continuation, or the reversal of trends established in the London and Asian sessions.
.png)
Risks and limitations of the ICT trading strategy
The ICT method offers valuable insights, but you can’t ignore its risks and limitations:
To successfully implement the ICT strategy, traders must wait for clear setups and strictly adhere to the risk management rules.
The ICT strategy is complex and anyone using it needs to make sense of technical analysis, price movements, liquidity pools, and the way big institutions move in the market.
The success of the ICT strategy depends on how well a trader reads market signals and makes precise, timely trades. Even if you stick to the strategy’s rules, getting the signals wrong or having poor trade execution means losing that position.
Potential disadvantages or challenges of using ICT
One of the biggest challenges with the ICT strategy is how complex it is. It covers a lot of different concepts, especially the numerous specifics of how the market works. Plus, it might not be the best fit for every trader. Those with less experience or limited time to really learn the methodology may struggle at first.
Tips for reducing risks and improving results
To manage risks and make the most of the ICT trading strategy, you need to use timeframe analysis, correctly identifying the setups on both higher and lower timeframes and following the overall trends. With trend following, the chances of a successful trade go up. Equally important, ensure your risk-reward ratio is balanced with your profitability for good risk management.
For example, a strategy with a 50% profitability rate and a risk-reward ratio of 1:2 can be effectively combined to form a successful trading approach.
It is important to understand that smart money concepts are not guarantees of success but principles that you need to backtest extensively. By backtesting strategies, you’ll set yourself up with reasonable expectations, and finetune your strategy effectively. Then you can rest easy, knowing your approach is based on tested methods rather than theoretical assumptions.
Summary
If you want to explore the ICT trading strategy, take the time to learn about its key components and why the markets move a certain way. Pay attention to fair value gaps, optimal trade entry points, and the dynamics of various trading sessions, and you’ll be better at anticipating changes in the market and institutional trading behavior. While the strategy is complex and comes with risks, you’ll be able to leverage its benefits for successful trading as you learn and experiment.
FAQ
Is ICT a good trading strategy?
Many traders find the ICT forex strategy effective because it provides a clear framework for market analysis. It focuses on interpreting market moves, the flow of institutional orders, and key price levels. That said, it can be a bit complicated, so it’s not the best fit for beginners who feel overwhelmed by the details.
What is the ICT silver bullet strategy?
The ICT silver bullet strategy is an intraday trading method designed to take advantage of big price movements in a short period. It focuses on pinpointing key liquidity levels and trading during specific times when the market tends to move predictably. This strategy seeks to profit from quick price shifts and is best used in markets with high liquidity.
What is the ICT market structure?
The ICT market structure is a tool for analyzing the market’s overall direction and behavior. It helps traders identify important phases like market manipulation, accumulation, and distribution. At the same time, it also helps spot changes in market trends. These shifts are marked by breaks in key price levels, which indicate potential trading opportunities.
What is the ICT trading strategy?
The ICT (Inner Circle Trader) strategy includes a range of methods and principles that are meant to boost trading performance. The idea is to tap into the behaviors and strategies used by institutional traders. It involves understanding ICT market structure, order flow, and key trading sessions.


.png)
.png)




.png)
.png)

.png)